Think about how you interact with others in school or college. You build friendships, form alliances, and make decisions based on trust, common interests, and sometimes competition. Countries do the same on a larger scale. They work with other nations to ensure security, trade, and global stability. The way a country decides to engage with others is called foreign policy.
Foreign policy is a government’s strategy for managing relationships with other countries and international organizations. It helps solve conflicts, build economic partnerships, and achieve national goals. But what influences these decisions? Various factors, known as the determinants of foreign policy, shape how a country interacts with the world.
What is Foreign Policy?
Foreign policy is the plan and approach a government uses when dealing with other countries and global organizations. It is mainly based on activities and actions that serve a country’s interests in relation to other nations. Essentially, foreign policy is the process through which a country decides what international actions to take.
It represents how a country responds to the world around it, both now and in the future. Foreign policy plays a key role in achieving a nation’s goals and protecting its interests.
Must Read Guide- An In-Depth Look at Public Policy Issues and 5 Examples
10 Most Important Determinants of Foreign Policy
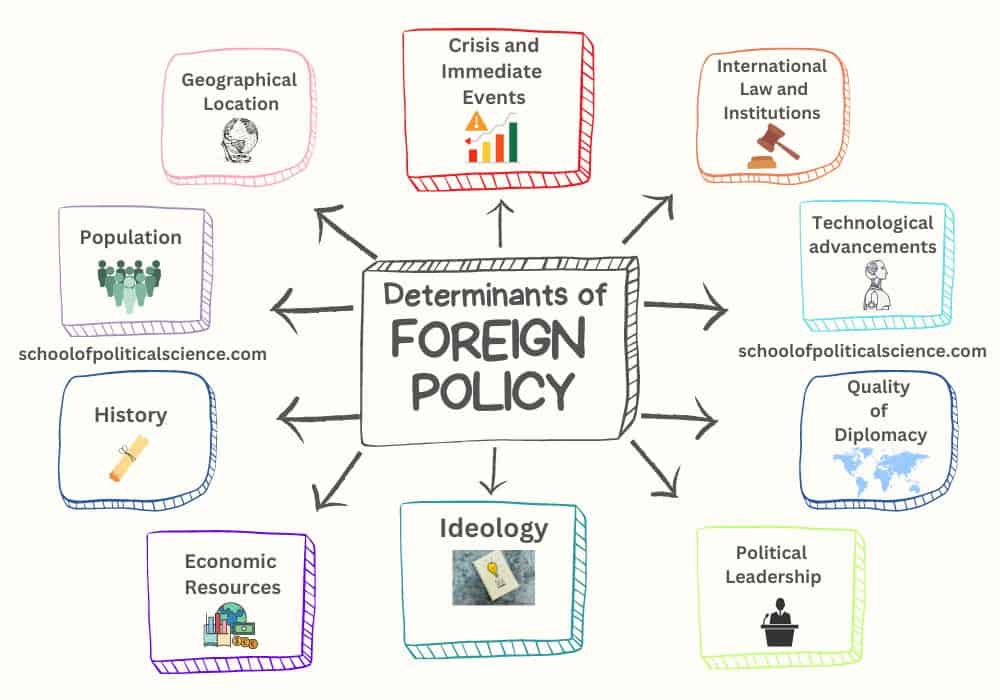
Every country creates a foreign policy to achieve certain goals on the global stage. This policy is not just based on the personal desires of leaders.
Leaders must carefully consider many factors when making foreign policy decisions. These factors are known as the “determinants of foreign policy.”
These determinants of foreign policy can vary from country to country, depending on their unique situation. Some factors are more important than others, but all play a role in shaping foreign policy. Here are some key factors that influence foreign policy decisions:
- Geographical Location
- Population
- History
- Economic Resources
- Ideology
- Government Efficiency and Political Leadership
- Diplomatic Strength
- Crises and Immediate Events
- Technological Advancements
- International Law and Organizations
1. Geographical Location
Geography plays an important role in shaping a country’s foreign policy in two ways: the physical environment and the political importance of its location.
The physical environment includes the size, climate, and terrain of the country. An ideal environment would have:
- Security: Countries with mountains or oceans as natural barriers are harder to invade.
- Trade: Nations near important trade routes or oceans have economic advantages.
- Climate: Weather conditions influence agriculture, economy, and even migration.
While it’s not possible to control a country’s geography, it still heavily influences foreign policy.
the United Kingdom’s Island geography has allowed it to develop a strong navy and trade networks, while the United States’ location helped it avoid European conflicts for much of its history.
2. Population
The size and quality of a country’s population affect its foreign policy. A large population can provide:
- Military power
- Workforce for economic growth
- Political influence in global affairs
For a long time, the size of a country’s population has been seen as a measure of its strength. For example, China’s large population helped it resist the United States during past wars.
The link between population and foreign policy is especially important when it comes to a country’s capabilities. A large population can help with unity, political organization, public awareness, political participation, and influencing government decisions. Public opinion can also pressure the government to make certain foreign policy choices.
However, the quality of the population is even more important than its size. The skills, abilities, and education of citizens help spread the country’s influence globally and also secure a sustainable economic growth.
3. History
A country’s past influences its present and future foreign policy decisions. Wars, colonial experiences, and past alliances shape national identity and diplomatic strategies.
For example, after World War II, Germany and Japan adopted peaceful foreign policies focused on economic development and global cooperation.
4. Economic Resources
A country’s foreign policy is heavily influenced by its economic resources. The economic strength of a nation shows how much it can afford to do and impacts its relations with other countries.
The main goal of a nation’s economy is to use its land, labor, capital, and businesses to produce goods. It also focuses on distributing wealth, ensuring public welfare, and improving citizens’ living standards.
Countries rich in natural resources can more easily achieve economic success. For example, oil has made the Middle East a key player in international politics.
Natural resources and industrial development are crucial for a country’s global standing. Today, a country’s power often depends on how industrialized it is and how many resources it has.
5. Ideology
Every country is guided by a specific political ideology, which shapes its values, policies, goals, and actions. This ideology not only influences a country’s internal affairs but also plays a big role in its foreign policy, making it a key factor in decision-making.
For example, socialist countries believe in promoting peace, friendship, cooperation, and non-interference in other countries’ internal matters.
On the other hand, capitalist countries often rely on exploitation and oppression both within their borders and globally. This is why capitalist countries tend to follow aggressive policies in areas like economics, politics, and culture. Some key ideologies include:
- Democracy: Countries like the U.S. and the European Union prioritize human rights and free trade.
- Socialism: Countries such as Cuba and North Korea focus on state control and self-reliance.
- Religious influence: Some nations base policies on religious principles, affecting their international relations.
6. Government Efficiency and Political Leadership
Government institutions’ effectiveness and leadership play a critical role in shaping foreign policy. Good leadership can:
- Strengthen global influence
- Prevent conflicts through diplomacy
- Respond effectively to crises
For instance, Franklin D. Roosevelt’s leadership during World War II helped form strong international alliances.
7. Diplomatic Strength
Diplomacy is essential for maintaining international relationships. Skilled diplomats help:
- Resolve conflicts peacefully
- Expand trade and alliances
- Represent national interests effectively
Countries with strong diplomatic networks often achieve their foreign policy objectives more smoothly.
8. Crisis and Immediate Events
Unexpected events can force countries to adjust their foreign policy quickly. Examples include:
- Wars and military conflicts
- Natural disasters
- Economic crises
- Pandemics and health emergencies
For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic changed global relations, leading to new health policies, trade restrictions, and vaccine diplomacy.
9. Technological Advancements
Technology plays a major role in foreign policy. Developments in:
- Communication (social media, digital diplomacy)
- Cybersecurity (protection against cyber threats)
- Military technology (drones, artificial intelligence in defense)
affect how countries interact and protect their interests.
10. International Law and Organizations
Global institutions like the United Nations (UN), World Trade Organization (WTO), and regional alliances influence foreign policy. Countries must follow treaties and agreements that regulate:
- Trade and economics
- Human rights policies
- Environmental protection
- International conflict resolution
For example, NATO membership influences a country’s defense policies and alliances.
Conclusion
Foreign policy is shaped by multiple factors that evolve over time. Some determinants, like geography and population, remain constant, while others, like crises and technological advancements, can shift rapidly. No single factor determines foreign policy; rather, a combination of these influences guides a country’s global decisions.
Understanding the determinants of foreign policy helps us see why countries act the way they do in global affairs. Nations that adapt effectively to these influences are more likely to succeed in protecting their interests and maintaining strong international relationships.
Let me share with you that you have learned from “10 Most Important Determinants of Foreign Policy“.
References
- Morgenthau, H. J. (2006). Politics Among Nations: The Struggle for Power and Peace. McGraw-Hill.
- Kissinger, H. (1994). Diplomacy. Simon & Schuster.
- Nye, J. S. (2011). The Future of Power. PublicAffairs.
- Waltz, K. N. (1979). Theory of International Politics. Addison-Wesley.
- Keohane, R. O. (1984). After Hegemony: Cooperation and Discord in the World Political Economy. Princeton University Press.
- United Nations. (2024). International Relations and Global Policies. www.un.org
- World Trade Organization. (2024). Trade and Foreign Policy Guidelines. www.wto.org
- U.S. Department of State. (2024). Foreign Policy Strategy Overview. www.state.gov
Must Read Guide


Comments are closed.