Have you ever wondered why people have different political beliefs or why certain political ideas last for generations? Think about your own political opinions—where did they come from? Did your family influence them? Or did school, friends, or social media shape your views?
The process that forms and transmits political beliefs over time is called political socialization, and it happens through various agents of political socialization.
Political socialization helps explain how political culture is created and sustained in society. It ensures that political values are passed down from one generation to the next, helping to maintain stability. Even as societies change, this process remains essential for political participation and engagement.
Must-Read– Political Culture: Meaning, Features, 4 Types, And Importance
What is Political Socialization?
Political socialization refers to the lifelong process through which individuals acquire political attitudes, beliefs, values, and behaviors. It is the process by which people develop their understanding of politics, political ideologies, and their role in the political system.
During political socialization, individuals absorb and internalize information about political institutions, parties, leaders, and policies from various sources such as family, education, media, peers, and religious institutions. These sources play a significant role in shaping individuals’ political opinions and values, influencing their political preferences, party affiliations, and participation in the political process.
It begins in childhood and continues throughout adulthood, as individuals encounter new experiences and engage with different social and political contexts.
Family, in particular, plays a crucial role in early political socialization, as children often adopt the political beliefs and behaviors of their parents or guardians.
Schools and educational institutions also play a significant role in political socialization by providing formal instruction on political systems, civics, and democratic values. Media, including news outlets and social media platforms, shape individuals’ political views by presenting information and framing political issues in particular ways.
Overall, it is a complex and ongoing process that influences individuals’ political identities, attitudes, and behaviors, shaping their understanding of political concepts, their participation in the political process, and their overall engagement with politics and society.
Must Read- Political Sociology: Understanding Its Meaning, Nature, and Scope
Key Characteristics of Political Socialization
Several important characteristics define It:
- It Transmits Political Culture: Political socialization ensures that a society’s political culture is preserved and passed down.
- It Educates Citizens: It helps people understand how their government works and their role within it.
- It is a Lifelong Process: While early childhood is a crucial stage, political socialization continues throughout life.
- It Happens in Different Ways: People learn political values through imitation (copying others), instruction (formal education), and motivation (encouragement to participate in politics).
- It Shapes Political Participation: Individuals develop loyalty to political systems and institutions through socialization.
- It Affects Everyone: All members of society experience political socialization at some level throughout their lives.
Agents of Political Socialization
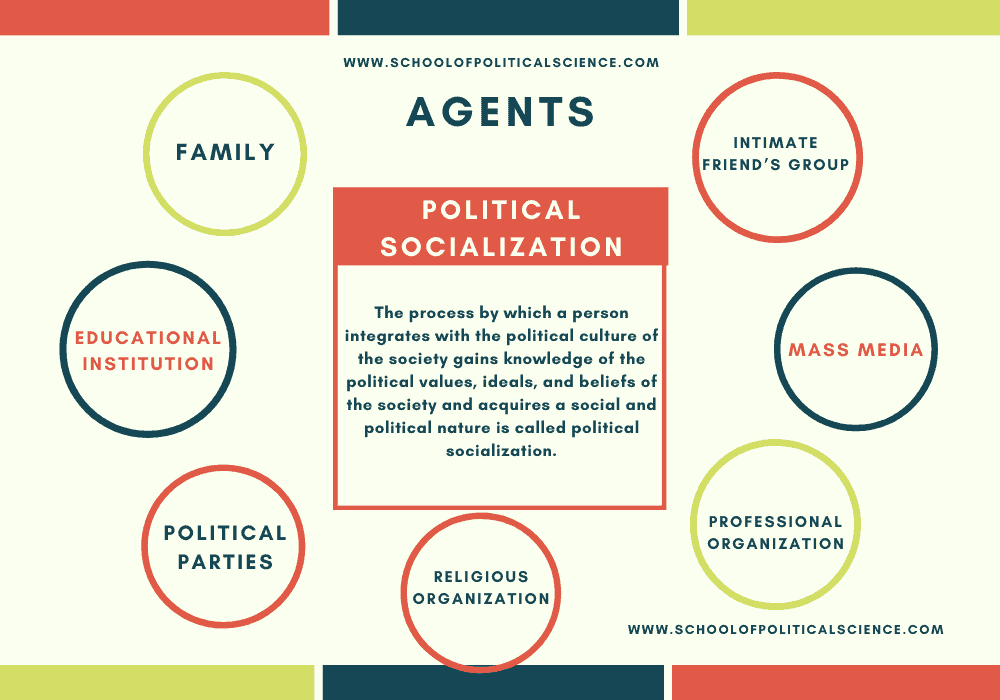
Few organizations play an important role in the context of political socialization. These are called agents of political socialization. They are also identified as the means of political socialization. These are:
- Family
- Intimate Friend’s Group
- Educational Institution
- Political Parties
- Mass Media
- Professional Organization
- Religious Organization
1. Family
The role of the family is important in transmitting political values from one generation to the next. In the first ten to fifteen years of his life in the family, the child acquires most of his political personality. The child takes note of the mentality of his parents and family and puts a deep and lasting strain on his mind. It is from the family that the child learns about its political values.
2. Intimate Friend’s Group
An intimate group is a group of people with similar or close friends or close friends. In modern times, industrialization, urbanization, and modernization have changed the way of life of the former; the number of problems has increased. So in modern society, the importance of intimate blinds has increased. There are many types of discussions with intimate friends. The political attitude of friends can influence and change a person’s moral outlook.
3. Educational Institution
After a few years of age, the child joined the educational establishment for education leavers and schools, colleges, and universities became important as a means of political socialization in his life. Attempts to increase loyalty to the country through the curriculum of the school include nationalist ideals, the past glory of the nation, discussions about the leaders of the nation, etc.
4. Political Parties
Political parties compete in elections by politically organizing for leverage of political power. People of different levels and classes are involved in different types of work for one political party. Political parties increase people’s skills and awareness. People’s political role depends on the economic, social, and political outlook of the political party and its relationship with the political system.
5. Mass Media
Influence of science and technology, in modern times, the media such as radio, film, television, internet, etc. are very advanced and play an important means in political socialization.
With the help of the media, news, commentary, and images related to political events quickly reach the masses. Members of the government or government party use the media to voice their views. Opposition parties and their members take the same path.
6. Professional Organization
Various organizations organized on a professional basis are labor unions, trade unions, peasant associations, teachers ‘associations, students’ unions, etc. These organizations do not get political power like political parties or participate in the electoral competition but try to preserve their professional interests by influencing the government’s decision-making process.
These organizations communicate political values and sentiments among their members through various claims and political socialization is possible.
7. Religious Organization
The political role of religious organizations in modern-day secular democratic states has diminished. Yet it turns out that they have some indirect role.
In many European states, opposition to state and educational institutions is seen in connection with Roman Catholic meditation. In India, Hindu, and Muslim religious organizations try to influence the political views of their members in various ways.
Importance of Political Socialization
Political socialization plays a major role in shaping stable political environments, especially in developing democracies. For example:
- In India, democratic values are reinforced through education, media, and political activism.
- In the United States, civic education and media play a role in maintaining democratic engagement.
- In former colonial nations, political socialization helps balance traditional governance with modern democratic structures.
As societies undergo modernization, urbanization, and globalization, it helps individuals adapt to political changes and stay engaged in civic life.
Many countries that are now developing were once ruled by European powers. Starting in the mid-20th century, they began gaining independence. Since these countries were familiar with European political systems, many of them adopted similar structures after independence. However, they also kept parts of their own traditional social and political systems.
It is important to it in these countries to understand how their political and social systems have developed over time, how much they have changed, and how political traditions are maintained in Western countries. Since society is always changing, discussing political socialization helps us see how these changes impact the political system.
Conclusion
Political socialization is related to the political stability of society. To maintain political stability in the process of modernization, industrialization, urbanization, and various other changes, it is necessary to focus on political socialization. Emphasis is placed on it in both liberal and socialist systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is political socialization important?
Political socialization ensures the transmission of political culture, educates citizens, promotes political stability, and encourages civic participation.
2. What are the main agents of political socialization?
The main agents include family, peer groups, educational institutions, political parties, mass media, professional organizations, and religious institutions.
3. How does political socialization occur?
Political socialization happens through observation, education, discussions, and engagement with political institutions and events.
4. At what age does political socialization begin?
It starts in early childhood and continues throughout life as individuals encounter new political experiences.
5. How does mass media influence political socialization?
Mass media shapes public opinion by presenting political news, debates, and narratives, influencing how people understand and engage with politics.
References
- Almond, G. A., & Verba, S. (1963). The Civic Culture: Political Attitudes and Democracy in Five Nations. Princeton University Press.
- Dawson, R. E., & Prewitt, K. (1969). Political Socialization: An Analytical Study. Little, Brown & Co.
- Greenstein, F. I. (1965). Children and Politics. Yale University Press.
- Niemi, R. G., & Hepburn, M. A. (1995). “The Rebirth of Political Socialization.” Perspectives on Political Science, 24(1), 7-16.
- Sigel, R. S. (Ed.). (1989). Political Learning in Adulthood: A Sourcebook of Theory and Research. University of Chicago Press.
By understanding political socialization, individuals can better evaluate their beliefs and make informed political choices.
Must Read-
- Meaning, Characteristics, And 5 Types of Sovereignty
- Political Theory And Why Should We Study Political Theory?
- 3 Most Important Types of Political Theory
- The Resurgence of Political Theory
- Meaning, History, Features, and Importance of Political Philosophy
Let me share with you that you have learned from globalization “Political Socialization: Meaning, Agents, and Importance“.

