Have you ever wondered why some days you feel highly motivated, while on other days, even the simplest task feels exhausting? Imagine a time when you were extremely hungry—did you feel like studying or working? Probably not! Your primary concern at that moment was to find food.
Now, think about a time when you were financially stable but felt lonely. In this situation, was money your main priority? Most likely, your focus was on relationships and companionship. This pattern of human motivation is beautifully explained by Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory.
Must Read Guide- Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory: Understanding Motivation in the Workplace
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory?
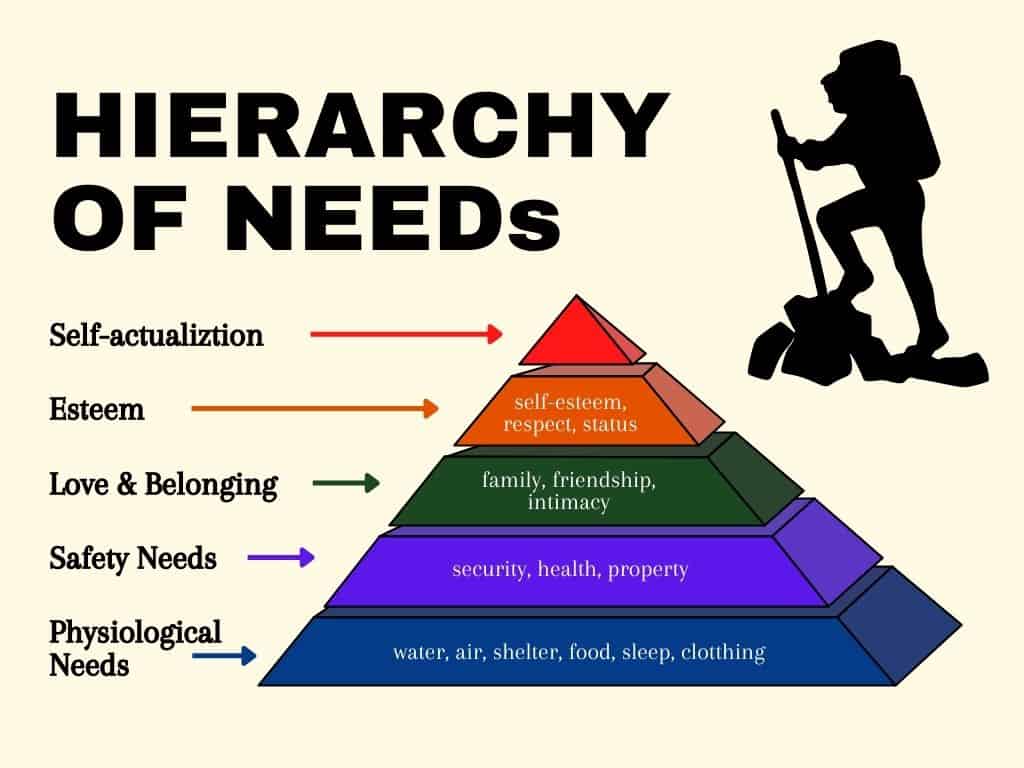
Proposed by psychologist Abraham Maslow in 1943, the hierarchy of needs explains human motivation through a five-tiered pyramid. Maslow suggested that people have a set of needs arranged in a hierarchical order, meaning lower-level needs must be satisfied before higher-level needs become a priority. The five levels are:
- Physiological Needs (Food, water, shelter, sleep)
- Safety Needs (Security, health, financial stability)
- Love and Belongingness Needs (Friendships, relationships, social connections)
- Esteem Needs (Self-respect, recognition, confidence)
- Self-Actualization Needs (Personal growth, creativity, fulfilling one’s potential)
Let’s explore each level in detail.
1. Physiological Needs – The Foundation of Survival
At the base of Maslow’s pyramid are physiological needs—the most basic and essential for survival. These include food, water, air, sleep, and shelter. If these needs are not met, the human body struggles to function properly.
Example: Imagine you’re in a desert with no water. Would you worry about your career or social life? No! Your only priority would be finding water. Similarly, a homeless person prioritizes food and shelter over social status.
In today’s world, many people still struggle to meet these basic needs. Poverty, malnutrition, and lack of access to clean water remain global issues. Governments and organizations work to address these problems by providing food aid, housing, and healthcare to vulnerable populations.
2. Safety Needs – The Need for Stability
Once physiological needs are satisfied, individuals seek safety and security. This includes physical safety, financial stability, good health, and protection from harm.
Example: Why do people invest in insurance, save money, or seek stable jobs? Because safety provides peace of mind. Without it, anxiety takes over, preventing progress to higher needs.
Safety is not just about personal security but also extends to larger social structures. Nations build armies and law enforcement agencies to protect citizens, and companies establish policies to ensure workplace safety. Even online safety has become a major concern, with cybersecurity playing a crucial role in protecting personal data and privacy.
3. Love and Belongingness Needs – The Need for Connection
Humans are social beings, and relationships play a crucial role in motivation. This level involves forming friendships, maintaining family bonds, and experiencing romantic relationships. A lack of belongingness can lead to loneliness and depression.
Example: Have you ever felt left out in a social gathering? That feeling of isolation stems from an unmet belongingness need. In contrast, being surrounded by supportive friends brings a sense of happiness and security.
In the digital era, social media plays a significant role in fulfilling or sometimes distorting these needs. While it helps people stay connected, it can also lead to feelings of inadequacy or isolation. It’s essential to strike a balance between virtual and real-life relationships to maintain genuine human connections.
4. Esteem Needs – The Need for Recognition
After securing social connections, people seek self-respect, recognition, and achievement. There are two types of esteem:
- Internal Esteem: Confidence, self-worth, and personal growth.
- External Esteem: Status, reputation, awards, and recognition from others.
Example: Athletes train rigorously not just for personal satisfaction but also for medals and recognition. Similarly, students strive for good grades to gain respect and acknowledgment.
Esteem needs are deeply tied to mental well-being. A lack of self-confidence can lead to anxiety and self-doubt, whereas excessive dependence on external validation can result in stress and burnout. This is why self-care, positive reinforcement, and setting personal goals are crucial in maintaining a healthy balance in life.
5. Self-Actualization – Becoming the Best Version of Yourself
At the top of Maslow’s pyramid is self-actualization—the desire to realize one’s full potential. This level is different for everyone. Some may seek creativity, while others may pursue knowledge, leadership, or innovation.
Example: Think about great personalities like Mahatma Gandhi, Albert Einstein, or Steve Jobs. Their motivation wasn’t just money or fame but the desire to make a difference.
Self-actualization is about pushing one’s limits and constantly striving for growth. It includes lifelong learning, artistic expression, and even spiritual enlightenment. While not everyone reaches this stage, those who do experience deep satisfaction and a sense of purpose.
Is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory Still Relevant Today?
Although proposed decades ago, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory remains highly relevant in modern psychology, workplace motivation, and personal development. Businesses apply this concept to improve employee satisfaction, and individuals use it for self-growth.
For example, companies that understand this hierarchy design workplaces that cater to their employees’ needs. Providing fair salaries (physiological and safety needs), fostering teamwork (belongingness needs), recognizing achievements (esteem needs), and encouraging professional development (self-actualization needs) can lead to higher productivity and job satisfaction.
Moreover, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory has been expanded to include self-transcendence, where individuals go beyond personal growth to help others achieve their potential. This is seen in philanthropy, mentorship, and leadership.
Applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory in Different Contexts
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory is not just limited to psychology—it has practical applications in various fields, including business, education, healthcare, and personal development.
Workplace Motivation
Employers use the hierarchy to improve employee satisfaction. Meeting basic salary needs (physiological), providing job security (safety), fostering teamwork (belongingness), recognizing achievements (esteem), and offering career development opportunities (self-actualization) can enhance productivity.
Education
Teachers apply Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory by ensuring students’ basic needs (nutrition, safety, and a positive learning environment) are met before focusing on academic achievements.
Healthcare
Medical professionals use this theory to prioritize patient care, addressing physical health first before psychological and emotional well-being.
Marketing & Consumer Behavior
Companies design marketing strategies by appealing to different levels of needs. For example, ads for insurance focus on safety needs, while luxury brands target esteem needs.
Criticisms and Limitations of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Despite its widespread use, Maslow’s theory has been criticized for being too simplistic and culturally biased. Some key criticisms include:
- Self-Actualization is Subjective: The concept of reaching one’s full potential differs from person to person.
- Lack of Scientific Evidence: Maslow’s theory is based on observation rather than empirical research.
- Cultural Differences: The hierarchy assumes a universal order of needs, but priorities vary across cultures.
- Flexibility of Needs: People often pursue higher-level needs even when basic ones are unmet.
Conclusion
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory remains a valuable framework for understanding human motivation. While it has limitations, its practical applications in psychology, business, and education make it a widely referenced theory. By recognizing and addressing different levels of needs, individuals and organizations can create environments that foster personal and collective growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can a person move back and forth between different levels of Maslow’s hierarchy?
Yes, life circumstances such as job loss, illness, or relationship changes can push a person up or down the hierarchy.
Q2: Is self-actualization achievable for everyone?
Not necessarily. It depends on individual aspirations, opportunities, and external factors influencing personal growth.
Q3: How does Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory apply to workplace motivation?
Employers can use it to ensure employees’ basic needs are met, provide job security, foster teamwork, and encourage career growth for increased productivity.
Q4: Does Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory apply to all cultures?
Not always. Different cultures may prioritize needs differently, and the hierarchy may not be universal.
Q5: Can multiple needs be pursued at the same time?
Yes, individuals often work towards satisfying multiple needs simultaneously, depending on their personal and environmental circumstances.
Let me share with you that you have learned from “Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory“
References
- Maslow, A. H. (1943). “A Theory of Human Motivation.” Psychological Review, 50(4), 370-396.
- Gawel, J. E. (1997). “Herzberg’s theory of motivation and Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.” Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation, 5(1), 11.
- Kenrick, D. T., et al. (2010). “Renovating the pyramid of needs: Contemporary extensions built upon ancient foundations.” Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5(3), 292-314.

